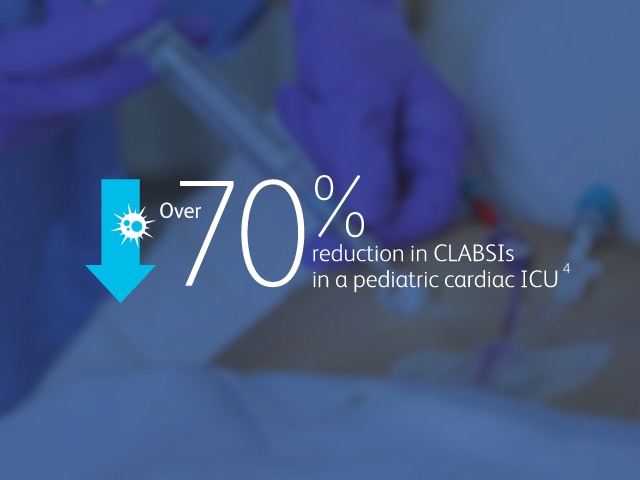
The BD MaxPlus™ Needle-free Connector is the only needle-free connector with an FDA-cleared label statement demonstrating a reduction in CLABSIs11
2013 CMS Hospital Compare data reported by 3,075 U.S. hospitals, accounting for nearly 11,000 CLABSIs associated with nearly 10 million catheter days, show that hospitals using the MaxPlus™ Needle-free Connector had lower unadjusted CLABSI rates, as well as lower standardized infection ratios, compared to hospitals not using the MaxPlus™ Needle-free Connector.1,3